Genes and you...
Written on Tuesday, June 27, 2006 by Gemini
Scientists Believe Both The Environment & Our Genes Influence The Person We Become. Genetics Has Become Controversial As Many Experts Worry That The Knowledge May Be Abused 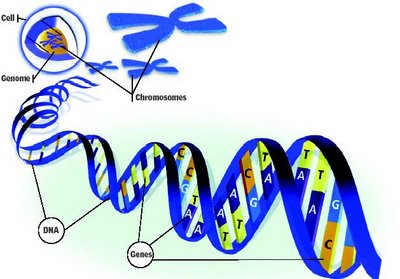
GENES IN OUR BODY
You have about 24,000 genes in nearly every one of your cells. Some are most active when you are growing, while others are active throughout your life. Your health depends on your genes, as well as on your diet and lifestyle
IDENTIFYING GENES
In the 1970s, scientists identified about 200 human genes. Recent advances in technology have speeded things up. By 1998 they had found over 6000 genes. In 1990, scientists started a huge international project that began with the aim of decoding all our genetic information by 2003: the Human Genome Project. A rough draft was completed in June 2000
THE HUMAN GENOME PROJECT
Your 24,000 different genes are your body’s instruction manual. They tell your body how to make all the proteins it needs to develop, survive and grow. Scientists taking part in the Human Genome Project aim to understand the contents of this manual, by locating and ‘reading’ each gene instruction
OUR CLOSEST ANIMAL RELATIVES
Our closest animal relatives are the great apes: chimpanzees, orangutans and gorillas. About 98% of the DNA in your genes is exactly the same as in chimpanzees, making you as closely related to a chimp as horses are to zebras. Chimps and humans share a common ancestor, who was probably swinging through the trees about 5 million years ago. Many other species of ape around at the same time eventually became extinct
DNA CLOCKS
As DNA passes from one generation to the next, it acquires small changes, known as mutations. Scientists estimate that after a million years, 2% to 4% of any stretch of animal DNA will have changed. By measuring the number of DNA changes between peoples from different parts of the world, scientists can calculate when they separated
FUTURE HEALTHCARE
Scientists and doctors hope to use genetic information to diagnose, treat, prevent and cure many deadly diseases like cancer, tuberculosis and even heart attack. Genes are instructions, which tell your body how to make all the proteins it needs to survive and grow. By identifying each of these proteins, scientists hope to understand how exactly the human body works, and what happens when the body develops a problem and doesn’t work properly
MODERN GENETICS AND BEHAVIOUR
Modern genetics research seeks, not to ‘improve’ human race, but to advance the health and choice of individuals. Of the 24,000 different genes in the human body, 30,000 are used in our brain cells. Scientists are only beginning to find out what all these genes do, how they work together and how they interact with our environment
DANGEROUS KNOWLEDGE
Do we really want to know how our genes influence our behaviour? The knowledge may lead to new ways of treating various disorders, but people may try to use it as an excuse for violent or criminal behaviour. Companies may use it to discriminate against certain people. There are also fears that in the future, in pursuit of a genetic ‘ideal’, parents will genetically ‘improve’ their kids by getting rid of ‘undesirable’ characteristics before they are born.

